Clojure Unit Testingλ︎
The function is the unit under test in Clojure. All public functions that form the API of their respective namespace should have a matching test, i.e. (deftest) definition.
clojure.test namespace provides functions for defining and running unit tests and is available in the Clojure library for any project to use.
Unit Test Principlesλ︎
- A
testnamespace for eachsrcnamespace under test - A
deftestfunction for each function under test, named after the function its testing with-testat the end of the name - Multiple assertions (
isare) for one function isdefines an assertion returning true (test pass) or false (test fail), typically a comparison between a known value and the result of a function callareto testing similar functionality with different data sets (or use generative testing)testingto logically group assertions and provide a meaningful description of that grouping (easier to identify tests when they fail)use-fixturesto call fixture functions that setup and tear down any state required for test(s) to run- Test API rather than implementation
- test generic helper or private functions through public functions of each namespace (minimise test churn and time to run all tests)
^:helpermeta-data ondeftestfor more generic functions, to skip those tests via a test selector- Use generative testing to create more maintainable test code with more extensive range of data
- Use test selectors with a test runner to selectively run tests and optimise speed of test runs
- Limit mocking of systems to integration tests (although mocking data is good everywhere)
Code should evaluate or have line comments
All Clojure code should be valid syntax and able to be evaluated (compiled), even code within a (comment ) expression or after a #_ reader comment.
Code commented with a line comment, ;;, will not be read by Clojure and cannot cause compilation errors when evaluated
Running testsλ︎
Test runners can run be run in the REPL used for development or run separately via the command line and continuous integration tasks.
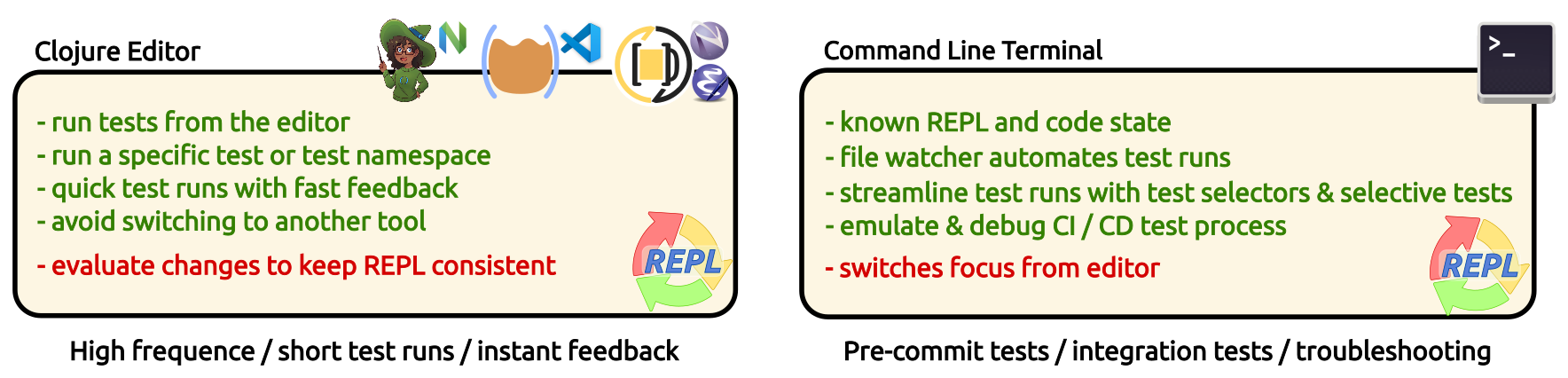
Run tests in Editor connected REPLλ︎
Using an editor connected REPL keeps the workflow in one tool and helps maintain focus. Using editor commands to run the tests and navigable error reports provides an effective flow to run and debug issues.
Ensure
testdirectory is on the class path when evaluating tests in the REPL, otherwise the(deftest)test definitions may not be found.
If functions or their associated tests are changed, they should be evaluated in the REPL before running tests to ensure those changes are loaded into the REPL.
If renaming a function or deftest, the original name should be removed from the REPL to avoid phantom tests (older definitions of tests that were evaluated in the REPL and still run, even though those tests are no longer in the source code).
Editors may include a command to remove function or test definitions, e.g. CIDER has undef command
The original name can also be removed using Clojure (ns-unmap 'namespace 'name), where namespace is where the name of the function or test is defined and name is the name of the function or test.
(ns practicalli.system-monitor) ; namespace definition
(defn dashboard [] ,,,) ; original function name
(defn dashboard-page [] ,,,) ; new function name
(undef 'practicalli.system-monitor 'dashboard) ; remove original function name
Stop and start the REPL process ensures all function and tests are correctly loaded
Command line test runnersλ︎
Command line test runners (i.e. koacha, Cognitect Labs) load function and test definitions from the source code files each time, ensuring tests are run and a clean REPL state is created on each run. This clearly defined REPL state is especially valuable for running repeatable integration tests.
Automate running the tests using a watch process, giving instant fast feedback, especially when displaying both the editor and test runner command line.
test runner can be configure to run only selective tests (i.e kaocha)
Run all tests (including integration tests) via the command line before pushing commits to ensure all changes to the code have been tested.
If tests are not running in the REPL or are returning unexpected errors, a command line test runner is a useful way to diagnose if it is the test code or test tools causing the error.
The CLI approach is also more robust for longer running tests than running within an editor.
Avoid stale tests
Running tests via a command line test runner will never experience stale tests, as long as all relevant changes are saved to the source code files.
Run tests in the REPLλ︎
clojure.test includes the run-tests function that runs tests (deftest definitions) in given namespaces and run-all-tests which runs all tests in all namespaces.
(run-all-tests) ; run all tests in all namespaces
(run-tests 'practicalli.system-monitor-test) ; run all tests in practicalli.system-monitor-test
run-testsandrun-all-testsare a less common approach as the command line and editor driven test runners provide a rich set of features
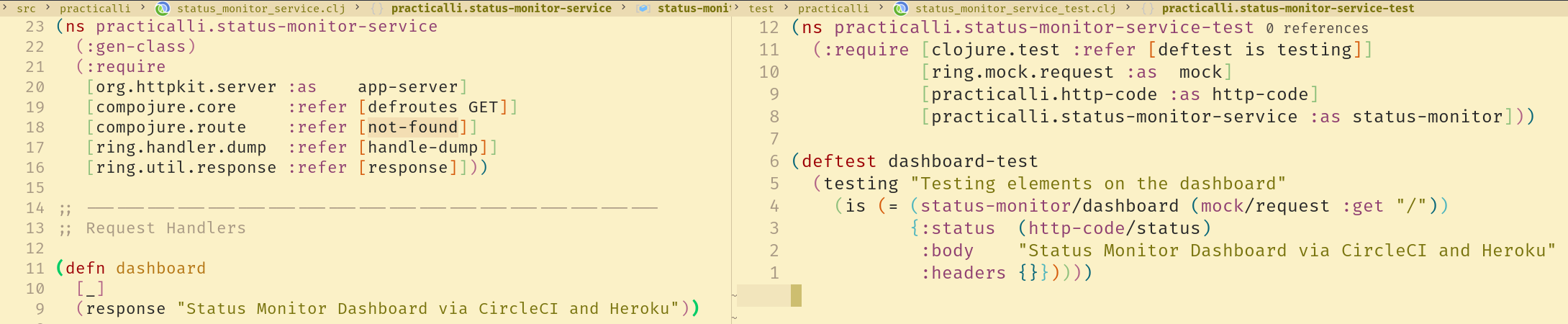
Project structure with testsλ︎
For each source code file in src there should be a corresponding file in test directory with the same name and _test postfix.
For example, code to test the src/codewars/rock_paper_scissors.clj is saved in the file src/codewars/rock_paper_scissors_test.clj file.
Example project: CodeWars: Rock Paper Scissors
Source and Test Namespacesλ︎
As with file names, the namespaces for each test code file is the same as the source code it is testing, with a -test postfix.
codewars/rock-paper-scissors source code namespace will have a matching codewars/rock-paper-scissors-test namespace.
Create Projects from templates
Templates typically include a parallel test and src directory structure. The clj-new tool has build it templates (app, lib) and will create src and test directories in the projects it creates.
clojure -T:project/new :template app :name practicalli/rock-paper-scissors-lizard-spock
Project Examples: Code challenges with unit testsλ︎
- TDD Kata: Recent Song-list - simple tests examples
- Codewars: Rock Paper Scissors (lizard spock) solution -
andexamples - practicalli/numbers-to-words - overly verbose example, ripe for refactor
- practicalli/codewars-guides - deps.edn projects
- practicalli/exercism-clojure-guides - Leiningen projects
Referencesλ︎
- Example based unit testing in Clojure - PurelyFunctional.tv