Java Host
Java is a host platform for Clojure, on which Clojure projects and tools run. Java provides a virtual machine which runs the bytecode generated when Clojure code is compiled.
Java virtual machine includes a Just In Time (JIT) compiler that optimises running of bytecode.
Practicalli recommends OpenJDK version 21
Install Javaλ︎
Check to see if there is an appropriate version of Java already installed.
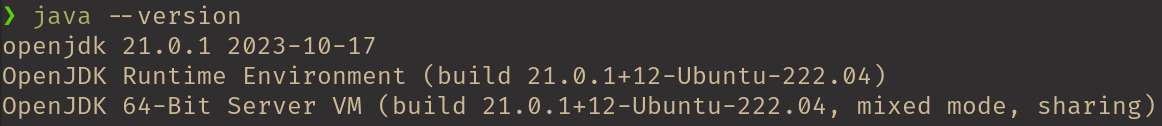
Open a terminal and run the command
If Java is installed and on the execution path, the version infomation is returned
Install Java development kit (JDK) using the apt package manager (login as su - or prefix the command with sudo)
Check available versions of OpenJDK
Long terms support versions should include OpenJDK 17 and may include OpenJDK 21. Check versions available via the apt package management tool.
Optionally include Java docs and sources
Install the openjdk-21-doc locally to provide Javadocs to support Java Interop code.
Install the openjdk-21-source package to support navigation of Java Object and Method source code, especially useful when using Java Interoperability from within Clojure code.
Practicalli Clojure CLI Config provides the :src/java17 alias to include the Java sources in the classpath when running a REPL.
If openjdk-21-jdk package is not available, add the Ubuntu OpenJDK personal package archive
When multiple versions of Java are installed, set the version using the update-alternatives command in a terminal
Available java versions will be listed. Enter the list number for the version you wish to use.
Using Homebrew, run the following command in a terminal to install Java 17:
Switching between Java versions
More than one version of Java can be installed on MacOSX. Set the Java version by opening a terminal and using one of the following commands
Show the Java versions installed
Switch to Java version 21
Alternatively, install JEnv Java version manager
For Windows 10 use Windows Subsystem for Linux and Windows Terminal are recommended if you have administrative privileges and are happy to use a Unix system on the command line.
Alternatively use scoop.sh, a command line installer for windows. Powershell 5 or greater is required.
Follow the scoop-clojure install instructions, summarized here:
scoop can also be used to install clojure
If neither Scoop or Windows Subsystem for Linux work, try the Chocolatey package manager. Install the Java Runtime (JRE) using the following command in a command line window
If Chocolatey does not work, then try the manual Java install.
Download OpenJDK from Adoptium - pre-build OpenJDK binaries freely available for multiple operating systems.
Run the file once downloaded and follow the install instructions.
Multiple versions of Javaλ︎

.java-version file containing the Java version number in the root of the project.
A little Java Knowledgeλ︎
Very little knowledge of the Java language or the Java Virtual Machine is required.
It is quite simple to call Java methods from Clojure, although there are a wealth of functions and libraries provided by Clojure and its community to minimise the need for Java Interoperability.
Reading stack traces may benefit from some Java experience, although its usually the first couple of lines in a stack trace that describe the issue.
Clojure uses its own build tools (Leiningen, Clojure CLI tools) and so Java build tool knowledge is not required.
When libraries are added to a project, they are downloaded to the $HOME/.m2 directory. This is the default Maven cache used by all JVM libraries.
clojure -Spom will generate a Maven pom.xml file used for deployment. Understanding of a minimal Maven POM (pom.xml) file is useful when managing issues with packaging and deployment.
The Java Virtual Machine is highly optimised and does not usually require any options to enhance its performance. The most likely configuration to supply to the JVM are to manage the amount of memory assigned, specifically for resource constrained environments.