journey to the edge of clojure

This article is a work in progress
Clojure CLI tools is a relatively new approach to creating an managing projects. The Edge project from JUXT takes the approach and extends it with its own features, such as being able to update projects created from the edge configuration.
Unlike Leiningen and Boot templates which are one of tasks, you can update a project you created a while ago with Edge and bring it up to date. It will be interesting to try this out in future articles.
Please see earlier articles in this series for background:
- Experimenting With Clojure CLI Tools Options
- A Deeper Understanding of Clojure CLI Tools
- Getting Started With Clojure CLI Tools
Installing JUXT Edge
You will need Clojure CLI tools installed to use Edge, so visit the Clojure.org - Getting Started page, or take a look at my article Getting Started With Clojure CLI Tools
Edge also has editor setup guides for Clojure for Atom, Emacs, Spacemacs, Intellij (Cursive), Vim and VS Code with Calva. There does not seem to be anything specific to Edge here though, so assume it doesnt require anything to be configured.
Using Emacs or Spacemacs, you may need to specify one or more aliases to use with Edge, so see my article on CIDER jack-in to Clojure CLI projects from Spacemacs
You also need to have a Git client installed.
Creating a project with Edge
If you are starting a new project, then you can simply create a local Git repository and add Edge as a remote repository and pull
mkdir my-project
cd my-project
git init
git remote add edge https://github.com/juxt/edge.git
git pull --allow-unrelated-histories --no-rebase edge master
Adding Edge to an existing project
A big difference to Boot and Leiningen templates is you can take an existing project and add Edge to it. So you can either clone a project or create a new project with clj-new if you have that installed.
Then just add Edge as a remote repository and pull.
git remote add edge https://github.com/juxt/edge.git
git pull --allow-unrelated-histories --no-rebase edge master
It will be interesting to try this approach out on older projects. I assume the project has to have a deps.edn file already (something interesting to test).
Creating a new app
Although we have added Edge to our new project, we dont yet have an app. There are examples you can run, but you probably want to create your own app rather than unpicking an existing one (also if the example updates, I am not sure what that would do to your changes).
Lets start with creating a simple Clojure api for our study group.
In the root of the project run the ./bin/app command and give it the name of your project. You need to specify a namespace with the overall domain (your company or GitHub account for example) and the project name. I am using practicalli as the domain namespace and study-guide-api as the project namespace.
./bin/app practicalli/study-guide-api
You should see output telling you the a new app has been created using the edge.app-template

A new directory has been created using the domain and project namespace names you provided. In our example, practicalli.study-guide-api
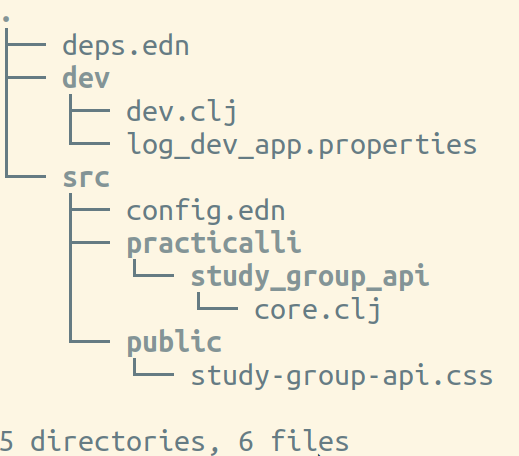
Starting the REPL
As we are using a Clojure project, we can start a REPL using by just including the :dev alias when we run Clojure on the command line.
clojure -A:dev
Take a look at the
deps.ednfile insidepracticalli.study-group-apidirectory for more options, especially if you create a ClojureScript or SASS project.
The project will download a noticable number of dependencies at this point, so time for a quick cup of peppermint tea...
Once the dependencies are downloaded you should see the standard clojure REPL.
I had expected rebel readline instead, but this is available when running the relevant Edge scripts, /bin/rebel. Keep in the practicalli.study-guide-api directory root and call the rebel script with the :dev alias.
../bin/rebel -A:dev
There will be just a few more dependencies to download, so this should be quick. You should see the rebel readline prompt as well as a message to call the (go) function.
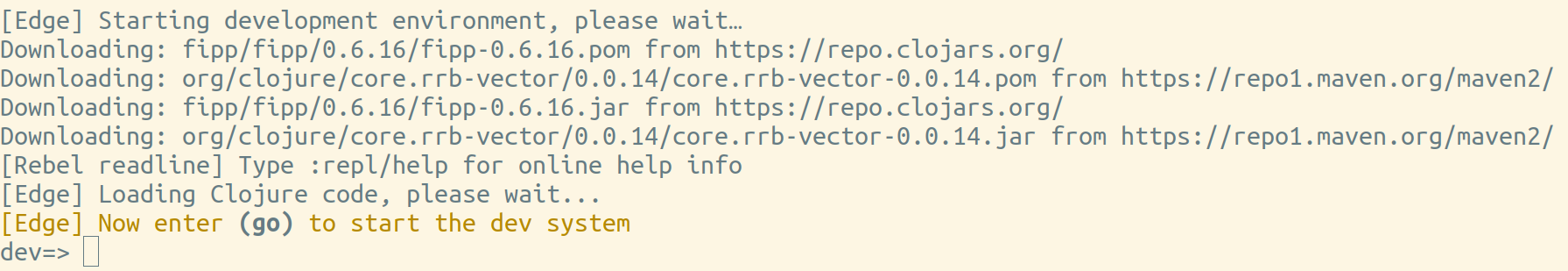
At the REPL prompt, type (go) to start the system for the application. This is a common approach for applications that have some component system to start/stop/reload your application or individual components of your application.
Open your browser at localhost:3636 to see the default project.
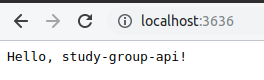
If you make any changes to the code you can reload them by calling (reset) in the REPL.
Adding a component and route
Samples taken from https://juxt.pro/edge/docs/first-component.html
Add a yada resource - its just a Clojure function
yada is a web library for Clojure, designed to support the creation of production services via HTTP.
(def hello-language
(yada/resource
{:methods
{:get
{:produces
{:media-type "text/plain"
:language #{"en" "zh-ch;q=0.9"}}
:response
#(case (yada/language %)
"zh-ch" "你好世界\n"
"en" "Life on the Edge")}}}))
Now we create a component for the yada resource for the web router to depend on.
To do this, we use defmethod on ig/init-key.
(defmethod ig/init-key ::hello-language [ ] hello-language)
The ig/init-key takes two arguments but we are not going to use them, so we can use the _ to provide an argument so the defmethod is valid but not use the argument values.
now update our system to include our new component. Open "src/config.edn" in your editor. Within the :ig/system map, add a key :practicalli.study-group-api.core/hello-language nil
Here is a brief explanation of the Integrant configuration file, config.edn
{:ig/system
{
;; component resources
:practicalli.study-group-api.core/hello-language nil
:practicalli.study-group-api.core/string "Hello, study-group-api!"
;; Integrant configuration for yada web listener
:edge.yada.ig/listener
{:handler #ig/ref :edge.bidi.ig/vhost
:port 3636}
;; Integrant
:edge.bidi.ig/vhost
[["http://localhost:3636"
;; routes
[""
[["/" #ig/ref :practicalli.study-group-api.core/string]
["/hello" #ig/ref :practicalli.study-group-api.core/hello-language]]]]]}}
Now back to the REPL and call (reset) to stop the app, load in the new resource and start again.
Unboxing Edge
Pulling edge into master will add a number of files
.gitignore
This contains patterns specific to the libraries this project uses, such at the .cpcache used by Clojure CLI tools and the .rebel_readline_history to keep a history of commands entered when running rebel readline based REPL.
**/.cpcache
**/.rebel_readline_history
**/.nrepl-port
**/target/*/**
**/log/*
!**/target/*/.gitkeep
# pack'd output
/*.jar
**/*.jar
There are 4 years worth of commits added, so if you wanted to see how Edge has evolved then fire up your favourite git client
Thank you. @jr0cket